ANALYSIS: By Mohammad Sadiq Sohail, an East-West Centre research specialist in Honolulu
Part 1 of a two-part series on the one-year anniversary of the Taliban takeover. Read part 2 tomorrow: The Taliban’s return has robbed Afghanistan’s women and girls of their future
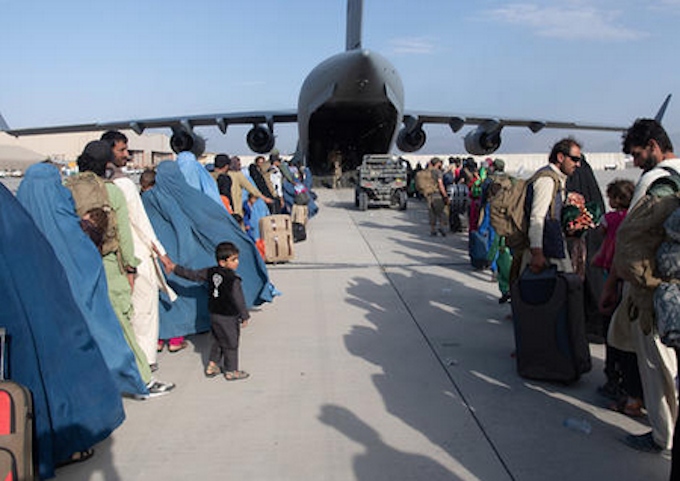
A year after the fall of Kabul and the end of the US military mission in Afghanistan, the country remains a place of misery.
No foreign government has recognised the Taliban as the legitimate government, and much of the modern economy has collapsed. The new rulers have not kept earlier promises, including high-school level education for girls and an amnesty for former Afghan government soldiers and civil servants.
Following a survey earlier this year, the United Nations pointed to many outrageous deficiencies in internationally recognised human rights. Moreover, the July 31 drone killing of 9-11 mastermind Ayman al-Zawahiri in a safe house in central Kabul showed that key elements of the Taliban leadership still harbour international terrorists, the original cause of the US intervention 21 years ago.
Fragile rule
Afghanistan seems trapped in a vicious circle, and the 38 million people living in the country are the frontline victims of a profound and still deepening tragedy. Without human rights, the Taliban regime will not enjoy UN membership, widespread diplomatic recognition, robust international humanitarian assistance or a broader base of legitimacy.
Without outside support, which financially accounted for 40 to 50 percent of the Afghan GNP prior to the Taliban takeover, Taliban rule remains fragile.
The one positive element in this bleak picture is that military violence has lessened. Despite some resistance from the competing Islamic State Khorasan terrorist group, or ISIS-K, and various other factions, Taliban rule appears unchallenged in the short term.
But in the longer term, the inflexibility and fragility of the Taliban authorities raise fundamental questions about whether their victory a year ago was just another phase in a longer civil war.
In some rural areas of the south long under Taliban control, life goes on much as before. But the loss of jobs in the more modern urban sectors and the scarcity of food has forced many Afghans back into an almost primitive economy, selling household possessions and sometimes even children to survive.
The world cannot simply wash its hands of this situation. There are three overriding US and NATO interests; ensuring that Afghanistan does not again becomes a haven and training ground for international terrorists; easing the world’s largest humanitarian/human rights crisis; and assisting endangered Afghans eligible for emigration.
Honoring US commitments
The al-Zawahiri case demonstrated the need for a strong reminder to the Taliban of their obligation not to harbour terrorists. However, this goes beyond monitoring known terror groups and must include steps to prevent the rise of a new generation of extremists. There are reports and video evidence of madrassa religious schools being established all over Afghanistan, primarily by Pakistani extremist groups.
This must be a high priority in any international discussions with the Taliban.
On the humanitarian and human rights fronts, in the wake of the al-Zawahiri case the US initially terminated talks with the Taliban over a possible release of former Afghan government financial reserves for humanitarian assistance. But recently American officials decided to go ahead with the talks after all, in light of fears over a looming hunger crisis in the coming winter months.
Other humanitarian assistance is needed, but must be administered through established international humanitarian groups, not the Taliban itself. Moreover, the world needs to remain united in not recognising the Taliban until they extend fundamental, universally-recognised human rights to all citizens, including female ones.
Finally, the United States needs to honour its commitments to the thousands of Afghans who loyally and bravely assisted US forces as doctors, technicians, interpreters or otherwise. Many such allies and their dependents remain in horrific or life-threatening positions in Afghanistan, some with US passports and others as qualified applicants under the Special Immigrant Visa (SIV) programme approved by Congress.
Some languish in third countries, such as Pakistan, waiting for their applications to be processed. While the US government has recently eased some of the burdensome entry requirements, more needs to be done to reach out to these people and assist in their release and successful integration into new host societies.
Mohammad Sadiq Sohail was an adviser to the Ministry of Justice and a university instructor in political science in Afghanistan before he was forced to leave the country following the Taliban takeover last August.