ANALYSIS: By Rhonda Garad, Monash University; Joanne Enticott, Monash University, and Rebecca Patrick, Deakin University
As we write this article, the delta strain of covid-19 is reminding the world the pandemic is far from over, with millions of Australians in lockdown and infection rates outpacing a global vaccination effort.
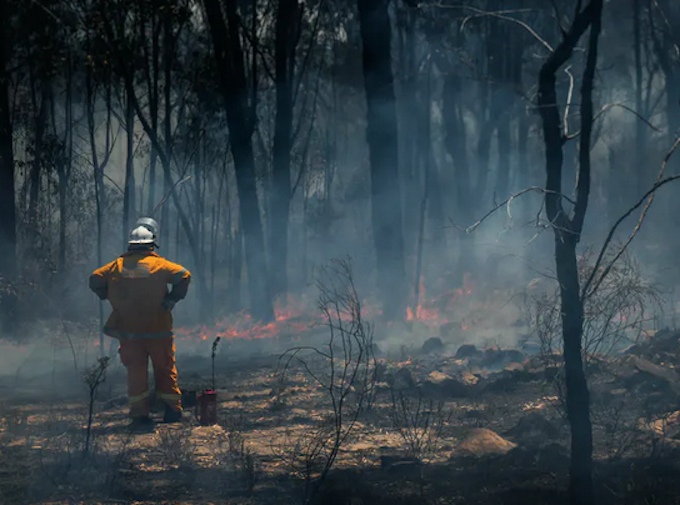
In the northern hemisphere, record breaking temperatures in the form of heat domes recently caused uncontrollable “firebombs”, while unprecedented floods disrupted millions of people.
Hundreds of lives have been lost due to heat stress, drownings and fire.
- READ MORE: The rise of ‘eco-anxiety’: climate change affects our mental health, too
- In a landmark judgment, the Federal Court found the environment minister has a duty of care to young people
- New polling shows 79 percent of Aussies care about climate change. So why doesn’t the government listen?
The twin catastrophic threats of climate change and a pandemic have created an “epoch of incredulity”. It’s not surprising many Australians are struggling to cope.
During the pandemic’s first wave in 2020, we collected nationwide data from 5483 adults across Australia on how climate change affects their mental health. In our new paper, we found that while Australians are concerned about covid-19, they were almost three times more concerned about climate change.
That Australians are very worried about climate change is not a new finding. But our study goes further, warning of an impending epidemic of mental health related disorders such as eco-anxiety, climate disaster-related post traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and future-orientated despair.
Which Australians are most worried?
We asked Australians to compare their concerns about climate change, covid, retirement, health, ageing and employment, using a four-point scale (responses ranging from “not a problem” to “very much a problem”).
A high level of concern about climate change was reported across the whole population regardless of gender, age, or residential location (city or rural, disadvantaged or affluent areas). Women, young adults, the well-off, and those in their middle years (aged 35 to 54) showed the highest levels of concern about climate change.
The latter group (aged 35 to 54) may be particularly worried because they are, or plan to become, parents and may be concerned about the future for their children.
The high level of concern among young Australians (aged 18 to 34) is not surprising, as they’re inheriting the greatest existential crisis faced by any generation. This age group have shown their concern through numerous campaigns such as the School Strike 4 Climate, and several successful litigations.
Of the people we surveyed in more affluent groups, 78 percent reported a high level of worry. But climate change was still very much a problem for those outside this group (42 percent) when compared to covid-related worry (27 percent).
We also found many of those who directly experienced a climate-related disaster — bushfires, floods, extreme heat waves — reported symptoms consistent with PTSD. This includes recurrent memories of the trauma event, feeling on guard, easily startled and nightmares.
Others reported significant pre-trauma and eco-anxiety symptoms. These include recurrent nightmares about future trauma, poor concentration, insomnia, tearfulness, despair and relationship and work difficulties.
Overall, we found the inevitability of climate threats limit Australians’ ability to feel optimistic about their future, more so than their anxieties about COVID.
How are people managing their climate worry?
Our research also provides insights into what people are doing to manage their mental health in the face of the impending threat of climate change.
Rather than seeking professional mental health support such as counsellors or psychologists, many Australians said they were self-prescribing their own remedies, such as being in natural environments (67 percent) and taking positive climate action (83 percent), where possible.
Many said they strengthen their resilience through individual action (such as limiting their plastic use), joining community action (such as volunteering), or joining advocacy efforts to influence policy and raise awareness.
Indeed, our research from earlier this year showed environmental volunteering has mental health benefits, such as improving connection to place and learning more about the environment.
It’s both ironic and understandable Australians want to be in natural environments to lessen their climate-related anxiety. Events such as the mega fires of 2019 and 2020 may be renewing Australians’ understanding and appreciation of nature’s value in enhancing the quality of their lives.
There is now ample research showing green spaces improve psychological well-being.
An impending epidemic
Our research illuminates the profound, growing mental health burden on Australians.
As the global temperature rises and climate-related disasters escalate in frequency and severity, this mental health burden will likely worsen. More people will suffer symptoms of PTSD, eco-anxiety, and more.
Of great concern is that people are not seeking professional mental health care to cope with climate change concern. Rather, they are finding their own solutions. The lack of effective climate change policy and action from the Australian government is also likely adding to the collective despair.
As Harriet Ingle and Michael Mikulewicz — a neuropsychologist and a human geographer from the UK — wrote in their 2020 paper:
For many, the ominous reality of climate change results in feelings of powerlessness to improve the situation, leaving them with an unresolved sense of loss, helplessness, and frustration.
It is imperative public health responses addressing climate change at the individual, community, and policy levels, are put into place. Governments need to respond to the health sector’s calls for effective climate related responses, to prevent a looming mental health crisis.
If this article has raised issues for you, or if you’re concerned about someone you know, call Lifeline in Australia on 13 11 14.![]()
By Dr Rhonda Garad, senior lecturer and research fellow in Knowledge Translation, Monash University; Dr Joanne Enticott, senior research fellow, Monash Centre for Health Research and Implementation (MCHRI), Monash University, and Dr Rebecca Patrick, director, Sustainable Health Network, Deakin University This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons licence. Read the original article.