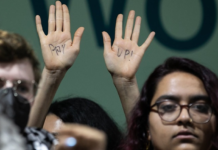Indonesia’s commitment to the Pacific continues to be strengthened. One of the strategies is through a commitment to resolving human rights cases in Papua, reports a Kompas correspondent who attended the Pacific International Media Conference in Suva earlier this month.
By Laraswati Ariadne Anwar in Suva
The Pacific Island countries are Indonesia’s neighbours. However, so far they are not very familiar to the ears of the Indonesian people.
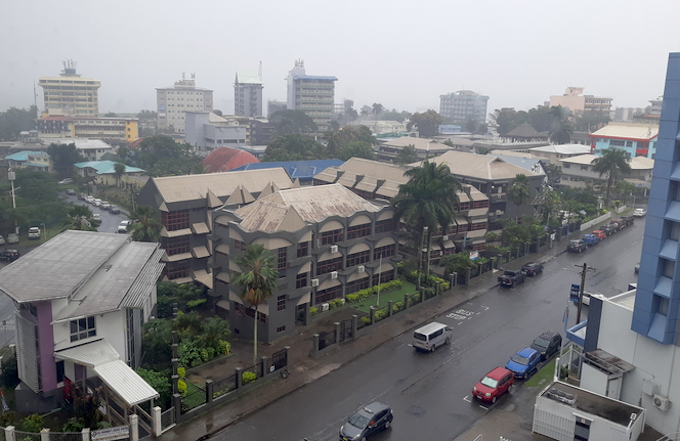
One example is Fiji, the largest country in the Pacific Islands. This country, which consists of 330 islands and a population of 924,000 people, has actually had relations with Indonesia for 50 years.
In the context of regional geopolitics, Fiji is the anchor of Indonesian diplomacy in the Pacific.
- READ MORE: When media freedom as the ‘oxygen of democracy’ and hypocrisy share the same Pacific arena — Pacific Media Watch
- Other Pacific Media Conference reports
Fiji is known as a gateway to the Pacific. This status has been held for centuries because, as the largest country and with the largest port, practically all commodities entering the Pacific Islands must go through Fiji.
Along with Papua New Guinea, Vanuatu, and the Front de Libération Nationale Kanak et Socialiste (FLNKS) of New Caledonia, Fiji forms the Melanesian Spearhead Group (MSG).
Indonesia now has the status of a associate member of the MSG, or one level higher than an observer.
For Indonesia, this closeness to the MSG is important because it is related to affirming Indonesia’s sovereignty.
Human rights violations
The MSG is very critical in monitoring the handling of human rights violations that occur in Papua. In terms of sovereignty, the MSG acknowledges Indonesia’s sovereignty as recorded in the Charter of the United Nations.
The academic community in Fiji is also highlighting human rights violations in Papua. As a Melanesian nation, the Fijian people sympathise with the Papuan community.
In Fiji, some individuals hold anti-Indonesian sentiment and support pro-independence movements in Papua. In several civil society organisations in Suva, the capital of Fiji, the Morning Star flag of West Papuan independence is also raised in solidarity.
/https%3A%2F%2Fasset.kgnewsroom.com%2Fphoto%2Fpre%2F2024%2F07%2F03%2F657788a7-cadf-42ac-82a2-49411a67dda5_jpg.jpg)
Even so, Fijian academics realise that they lack context in examining Indonesian problems. This emerged in a talanoa or focused discussion with representatives of universities and Fiji’s mainstream media with a media delegation from Indonesia. The event was organised by the Indonesian Embassy in Suva.
Academics say that reading sources about Indonesia generally come from 50 years ago, causing them to have a limited understanding of developments in Indonesia. When examined, Indonesian journalists also found that they themselves lacked material about the Pacific Islands.
Both the Fiji and Indonesian groups realise that the information they receive about each other mainly comes from Western media. In practice, there is scepticism about coverage crafted according to a Western perspective.
“There must be open and meaningful dialogue between the people of Fiji and Indonesia in order to break down prejudices and provide space for contextual critical review into diplomatic relations between the two countries,” said Associate Professor Shailendra Singh, a former journalist who is now head of the journalism programme at the University of the South Pacific (USP). He was also chair of the 2024 Pacific International Media Conference Committee which was attended by the Indonesian delegation.
‘Prejudice’ towards Indonesia
According to experts in Fiji, the prejudice of the people in that country towards Indonesia is viewed as both a challenge and an opportunity to develop a more quality and substantive relationship.
/https%3A%2F%2Fasset.kgnewsroom.com%2Fphoto%2Fpre%2F2024%2F07%2F14%2Fd960bec3-b0be-4507-9fee-19ebcc62e090_jpg.jpg)
In that international conference, representatives of mainstream media in the Pacific Islands criticised and expressed their dissatisfaction with donors.
The Pacific Islands are one of the most foreign aid-receiving regions in the world. Fiji is among the top five Pacific countries supported by donors.
Based on the Lowy Institute’s records from Australia as of October 31, 2023, there are 82 donor countries in the Pacific with a total contribution value of US$44 billion. Australia is the number one donor, followed by China.
The United States and New Zealand are also major donors. This situation has an impact on geopolitical competition issues in the region.
Indonesia is on the list of 82 countries, although in terms of the amount of funding contributed, it lags behind countries with advanced economies. Indonesia itself does not take the position to compete in terms of the amount of funds disbursed.
Thus, the Indonesian Ambassador to Fiji, Nauru, Kiribati, and Tuvalu, Dupito Simamora, said that Indonesia was present to bring a new colour.
“We are present to focus on community empowerment and exchange of experiences,” he said.
An example is the empowerment of maritime, capture fisheries, coffee farming, and training for immigration officers. This is more sustainable compared to the continuous provision of funds.
Maintaining ‘consistency’
Along with that, efforts to introduce Indonesia continue to be made, including through arts and culture scholarships, Dharmasiswa (a one-year non-degree scholarship programme offered to foreigners), and visits by journalists to Indonesia. This is done so that the participating Fiji community can experience for themselves the value of Bhinneka Tunggal Ika — the official motto of Indonesia, “Unity in diversity”.

Indonesia has also offered itself to Fiji and the Pacific Islands as a “gateway” to Southeast Asia. Fiji has the world’s best-selling mineral water product, Fiji Water. They are indeed targeting expanding their market to Southeast Asia, which has a population of 500 million people.
The Indonesian Embassy in Suva analysed the working pattern of the BIMP-EAGA, or the East ASEAN economic cooperation involving Indonesia, Malaysia, Brunei Darussalam and the Philippines. From there, a model that can be adopted which will be communicated to the MSG and developed according to the needs of the Pacific region.
In the ASEAN High-Level Conference of 2023, Indonesia initiated a development and empowerment cooperation with the South Pacific that was laid out in a memorandum of understanding between ASEAN and the Pacific Islands Forum (PIF).
At the World Water Forum (WWF) 2024 and the Island States Forum (AIS), the South Pacific region is one of the areas highlighted for cooperation. Climate crisis mitigation is a sector that is being developed, one of which is the cultivation of mangrove plants to prevent coastal erosion.
For Indonesia, cooperation with the Pacific is not just diplomacy. Through ASEAN, Indonesia is pushing for the ASEAN Outlook on the Indo-Pacific (AOIP). Essentially, the Indo-Pacific region is not an extension of any superpower.
All geopolitical and geo-economic competition in this region must be managed well in order to avoid conflict.
Indigenous perspectives
In the Indo-Pacific region, PIF and the Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA) are important partners for ASEAN. Both are original intergovernmental organisations in the Indo-Pacific, making them vital in promoting a perception of the Indo-Pacific that aligns with the framework and perspective of indigenous populations.
On the other hand, Indonesia’s commitment to the principle of non-alignment was tested. Indonesia, which has a free-active foreign policy policy, emphasises that it is not looking for enemies.
However, can Indonesia guarantee the Pacific Islands that the friendship offered is sincere and will not force them to form camps?
At the same time, the Pacific community is also observing Indonesia’s sincerity in resolving various cases of human rights violations, especially in Papua. An open dialogue on this issue could be evidence of Indonesia’s democratic maturity.
Republished from Kompas in partnership with The University of the South Pacific.