ANALYSIS: By Binoy Kampmark
Children should not pay for the sins of their parents. But in some cases, a healthy suspicion of the offspring is needed, notably when it comes to profiting off ill-gotten gains.
It is certainly needed in the case of Filipino politician and presidential candidate Ferdinand “Bongbong” Marcos Jr, who stands to win today if opinion polls are to be believed.
Bongbong’s father was the notorious martial law strongman Ferdinand Marcos; his mother, the avaricious, shoe-crazed Imelda.
- READ MORE: ‘Our blood is boiling’ – victims angry as dictator’s son edges closer to Philippine presidency
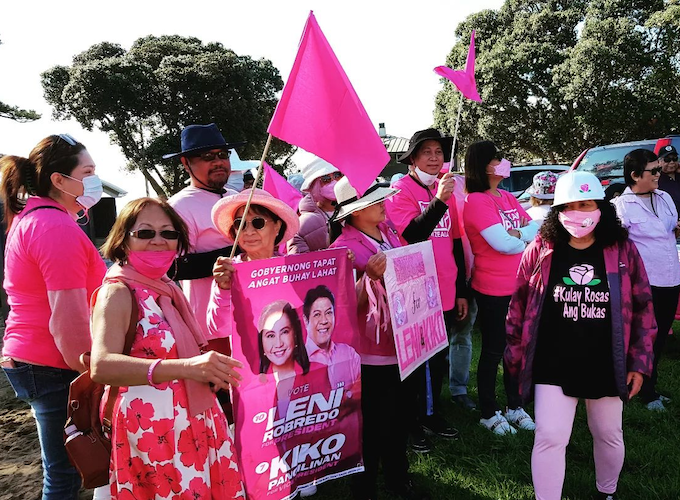
- Robredo’s plea to 412,000 in Pasay – 200 in Auckland: Fight fake news
- Other Philippine presidential elections
- Today’s Rappler livestream coverage
Elected president in 1965, Ferdinand Marcos indulged in murder, torture and looting. He thrived on the terrain of violent, corrupt oligarchic politics, characterised by a telling remark from the dejected Sergio Osmenã Jr, whom he defeated in 1969: “We were outgunned, outgooned, and outgold.”
In 1972, martial law was imposed on the pretext of a failed assassination attempt against the defence secretary, an attack which saw no injuries nor apprehension of suspects. It was only formally lifted in 1981.
Under the blood-soaked stewardship of the Marcos regime, 70,000 warrantless arrests were made, and 4000 people killed.
The Philippines duly declined in the face of monstrous cronyism, institutional unaccountability and graft, becoming one of the poorest in Southeast Asia. While Marcos Sr’s own official salary never rose above US$13,500 a year, he and his cronies made off with $10 billion. (Estimates vary.)
Garish portraits, designer shoes
When revolutionaries took over the Presidential palace, they found garishly ornate portraits, 15 mink coats, 508 couture gowns and more than 3000 pairs of Imelda’s designer shoes.
Fleeing the Philippines in the wake of the “people power” popular insurrection of 1986 led by supporters of Corazon “Cory” Aquino, the Marcoses found sanctuary in the bosom of US protection, taking up residence in Hawai’i.
Opinion polls show that Bongbong is breezing his way to office, a phenomenon that has little to do with his personality, sense of mind, or presence.

A Pulse Asia survey conducted in February showed voter approval at an enviable 60 percent. This would suggest that the various petitions seeking to disqualify him have had little effect on perceptions lost in the miasma of myth and speculation.
All this points to a dark combination of factors that have served to rehabilitate his family’s legacy.
For the student aware of the country’s oligarchic politics, this is unlikely to come as shocking. For one, the Marcoses have inexorably found their way back into politics, making their way through the dynastic jungle.
Imelda, for all her thieving ways, found herself serving in the House of Representatives four times and unsuccessfully ran for the presidency in 1992. Daughter Imee became governor of the province of Ilocos Norte in 2010, and has been serving as a senator since 2019.
Contested the vice-presidency – and lost
Marcos Jr followed a similar trajectory, becoming a member of congress and senator and doing so with little distinction. In 2016, he contested the vice-presidency and lost.
Bongbong has already done his father proud at various levels, not least exhibiting a tendency to fabricate his past. On the touchy issue of education, Oxford University has stated at various points that Marcos Jr, while matriculating at St Edmund Hall in 1975, never took a degree in Politics, Philosophy and Economics — as he claims.
According to the institution’s records, “he did not complete his degree, but was awarded a special diploma in Social Studies in 1978″.
A statement from the Oxford Philippines Society remarks that, “Marcos failed his degree’s preliminary examinations at the first attempt. Passing the preliminary examinations is a prerequisite for continuing one’s studies and completing a degree at Oxford University”.
The issue was known as far back as 1983, when a disturbed sister from the Religious of the Good Shepherd wrote to the university inquiring about the politician’s credentials and received a letter confirming that fact.
Outgoing President Rodrigo Duterte, whose own rule has been characterised by populist violence and impunity, has played his role in the rehabilitative process. In 2016, almost three decades after the former dictator died in Hawai’i, Duterte gave permission for Ferdinand Marcos to be buried with full military honours in Manila’s National Heroes’ Cemetery.
The timing of the burial was kept secret, prompting Vice-President Leni Robredo to describe the ceremony as “a thief in the night”.
‘Legitimising’ massive violations of human rights
A coalition of Jesuit groups claimed that the interring of Marcos in Manila “buries human dignity by legitimising the massive violations of human and civil rights… that took place under his regime.” Duterte would have appreciated the mirror-effect of the move, a respectful nod from one human rights abuser to another.
Under his direction, thousands of drug suspects have been summarily butchered.
Bongbong has also taken the cue, rehabilitating his parents using a polished, digital campaign of re-invention that trucks in “golden age” nostalgia and delusion.
Political raw material has presented itself. The gap between the wealthy and impoverished, which his father did everything to widen, has not been closed by successive governments. According to 2021 figures from the Philippine Statistics Authority, 24 percent of Filipinos — some 26 million people — live below the poverty line.
Videos abound claiming that his parents were philanthropists rather than figures of predation. The issue of martial law brutality has all but vanished in the narrative.
Social media and online influencers have managed the growth of this image through a coordinated campaign of disinformation waged across multiple platforms.
Gemma B. Mendoza of the Philippine news platform Rappler has noted the more sinister element of these efforts. Even as the legacy of a family dictatorship is being burnished, the press and critics are being hounded.
Robredo the only challenge
The only movement standing in the way of the Marcos family is Vice-President Robredo, who triumphed over Marcos Jr in 2016. Her hope is a brand of politics nourished by grassroots participation rather than shameless patronage.
The same cannot be said of the political classes who operate on the central principle of Philippine politics: impunity.
This, at least, is how political scientist Dr Aries Arugay, an associate professor of the University of Philippines, sees it: “We just don’t jail our politicians or make them accountable … we don’t punish them, unlike South Korean presidents.”
The opposite is the case, and as the voters make it to the ballot today, the country, if polls are to be believed, will see another Marcos in the presidential palace.
Dr Binoy Kampmark was a Commonwealth Scholar at Selwyn College, Cambridge. He currently lectures at RMIT University in Melbourne, Australia.