ANALYSIS: By Denis Muller, The University of Melbourne
There has been a lot of talk lately about the need for cultural change in Australia’s Parliament House. While that is incontestably necessary, there needs to be a cultural change in the media too.
The central power of the media is the power to portray. Portrayal through the media creates the pictures in our heads about people, events, ideas and organisations beyond our personal knowledge.
In his classic book Public Opinion, published in 1922, the American journalist and political philosopher Walter Lippmann wrote eloquently about this form of media power and its effect in creating stereotypes.
- READ MORE: Has Christian Porter been subjected to a ‘trial by media’? No, the media did its job of being a watchdog
- View from The Hill: Morrison sets up his own women’s network but will it produce the policy goods?
Stereotypes take root as deeply in the minds of journalists as anywhere else. They come in handy for reporters and subeditors under pressure to produce and publish under tight deadlines, and find expression through cliché, word-association and puns.
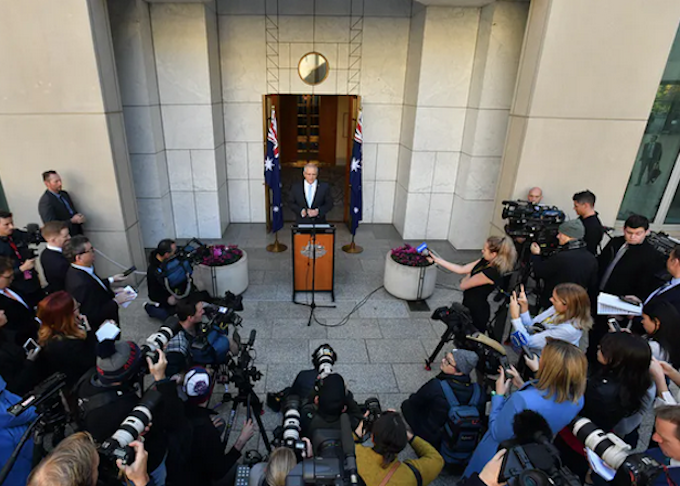
So it was that Sydney’s Daily Telegraph ran a headline on the story of Scott Morrison’s cabinet reshuffle saying:
Fair go for fairer sex as PM shuffles deck.
The portrayal of women as the “fairer sex” – embodiments of chastity and gentleness – is one of the most enduring stereotypes in Western culture. It can be traced back to the Gothic ideal of courtly love.
Today it is, at very least, condescending. It perpetuates the stereotype of women as powerless creatures needing protection or deserving reverential deference.
Lack of reflective thought
Given contemporary levels of violence against women and their treatment as sexual objects, it reveals a complete lack of reflective thought about the experiences of women who have been victims of violence and violation.
Words, portrayal, stereotypes: their interconnections shape culture, culture shapes attitudes and attitudes influence behaviour.
However, the media’s response to the crisis engulfing the government is not confined to thoughtless headlines and reflects far worse problems.
These were illustrated by the deliberate ravings of an Adelaide commercial radio broadcaster, Jeremy Cordeaux, sacked after referring to Brittany Higgins as “a silly little girl who got drunk”.
The fact that he was sacked is perhaps a sign that some in the media have grasped a shift in community standards concerning the portrayal of women.
When another shock jock, Sydney’s Alan Jones, proposed in 2011 that the then prime minister, Julia Gillard, be thrown out to sea in a chaff bag, he sailed through the ensuing storm undisturbed, although his show’s advertising revenue fell away.
The wave of outrage over the treatment of women in federal parliament is also putting internal strain on the media.
Press gallery gender balance
There has been a significant change over the past 20 years in the gender balance of the Canberra press gallery.
When the journalist and author Margaret Simons wrote a monograph, Fit to Print: Inside the Canberra Press Gallery in 1999, she referred to a class of senior journalists there as “God correspondents”. There was just one woman in this pantheon: Michelle Grattan.
Today, she might also include Laura Tingle, Katharine Murphy, Karen Middleton, Samantha Maiden from within the gallery, as well as Leigh Sales and Louise Milligan from outside who contribute influential coverage of national politics.
There are plenty of senior male correspondents too, but the shift in the gender balance at the top is there to be seen.
What looks like signs of strain within the gallery over this shift appeared in the Australian Financial Review on March 31.
The headline read: “PM caught in crusade of women journos”; the sub-heading “Anger at the government over the abuse of women is being led by a powerful group of female journalists”.
Not only was this a clear focus on the gender of gallery members, but it suggested women in the gallery were using their position to promote a feminised political agenda.
Maiden the real target
However, it soon became obvious that the real target of the article was news.com.au’s Samantha Maiden. It was her run of scoops, the article said, that had left the Morrison government in disarray.
The article went on to portray Maiden as a difficult colleague, and even trespassed on the privacy of her health. It belittled her as “a woman making a professional comeback” – from what we are left to guess.
It was written by a man described in the byline as “senior correspondent”.
Whether the Canberra press gallery is fracturing along gender lines over the issue of violence against women is an interesting question, not because it is about journalists but because it would have implications for the choices made by them about what stories to prioritise and how to tell them.
That in turn would influence the words, images and stereotypes coming out of the gallery, with consequences for how the voting public might respond.
An Essential Media poll taken for The Guardian Australia and published on March 30 showed Morrison’s approval rating among women voters has fallen 16 points since the Higgins story broke in February, while his standing with male voters has remained unchanged.
Those pictures in our heads really matter.![]()
Dr Denis Muller is a senior research fellow at the Centre for Advancing Journalism, The University of Melbourne. This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons licence. Read the original article.